Team I Gene Prediction Group
Members: Maria Ahmad, Hira Anis, Jessica Mulligan, Priya Narayanan, Aaron Pfennig, Winnie Zheng
Introduction
Prokaryotic Gene Feature
- Prokaryotic genes have a relatively well-understood promoter sequence, such as a regulatory sequence, which can regulate the transcription of the gene into an mRNA.
- Each prokaryotic gene has open reading frames(ORF) which start with start codons and end with end codons with no interruptions(end-codons) in-between, so it can provide a good, but not assured prediction of the protein-coding regions.
Gene Prediction
Gene prediction or gene finding is a process of identifying the regions of genomic DNA that encode genes. It is devised two-classes of methods that use similarity-based(homology) searches and Ab-initio prediction to capture the compositional differences among coding regions which will be translated into protein and noncoding DNA which can be translated into tRNAs and rRNAs.
Project Goal
The main goal of our project is to finish the gene prediction for the assembled gene from E.coli given by the previous group.
Methods
Ab-initio Methods(CDS prediction)
- Features of Predicting protein-coding genes
- ORFs
- Signal Sensor: Regulatory motifs(RBS, SD, etc)
- Content Sensor: The codon usage bias, based on GC content, can help to distinguish coding sequence from surrounding non-coding sequence.
- Markov and Hidden Markov Model
- Markov model is a stochastic model that can model the dynamics of systems. This system is made up of known states with a known transition probability which depends only on current states. In other words, the future state depends only on the current state, not the previous one.
- Hidden Markov Model(HMM) is described as a Markov model of random changing systems that is made up of unobserved(hidden) states. This model can determine state transition probability which is the probability between each hidden state and generate observable nucleotides.
- GeneMarkS2
- Self-training algorithm based on an HMM.
- Models transcription domain to predict gene start more accurately.
- incl. heuristic model designed to predict horizontally transferred genes.
- Pros and cons: GMS2 can have the highest sensitivity and specificity among different tools, but works on different gene regulatory motifs using learered and leaderless transcription.
./run_gms2.sh <path_to_genome>
- Glimmer3
- The Interpolated Markov Model(IMM) is at the core of Glimmer.
- Scoring the ORFs in reverse (stop codon back toward the start codon) relying on k-mer within the coding region.
- Trains on long ORFs.
- Pros and cons: Glimmer3 performs by most metrics but predicts the least short genes (<150 nt).
./run_glimmer3.sh <path_to_genome>
- Prodigal
- Identifying all ORFs and scores them using a dynamic programming approach.
- Refines predictions after training on the subset of ORFs.
- Pros and cons: Prodigals are trained on E.coli but predict the most genes start correctly in E.coil.
Tool Evaluation
Ab-initio Tools
- Use a reference gene, Escherichia_coli_cft073.ASM744v to test each tool by computing sensitivity(SN), positive predictive value(PPV) and specificity(SP) which only for start site prediction.
Calculation:
- SN = TP / (TP + FN)
- PPV = TP / (TP + FP)
- SP = TN / (TN + FP) (only start site prediction)
- TP=True Positive; TN=True Negative; FP= False Positive; FN=False Negative
Testing Results:
- The percentage of sensitivity, specificity and positive predictive value(only for the start site) were summarized on the following table. We also include the number of genes and running time in order to provide a stronger evaluation.
- GMS2 has higher sensitivity and start site positive predictive value. Prodigal has the shortest running time. At the same time, the Glimmer has the highest specificity.
Table 1. The performance evaluation for each tool by reference gene.
- On the 50 assembled genomes, comparing the predictions of GMS2, Prodigal, and Glimmer3 is to overlap each tool.
Figure 3. The overlapping of GMS2, Prodigal, and Glimmer results.
Testing Results:
- Generally, the tools greatly overlap.
- Glimmer predicts several unique genes not predicted by the others.
- Prodigal and GMS2’s predictions have a large overlap.
Results
Ab-initio
- Performed a BLAST search of the predicted genes against SwissProt database
./make_diamond_db.sh ./run_diamond.sh
- Filtered BLAST results by >90% coverage of query to:
- Plot ratio of predicted genes with BLAST support
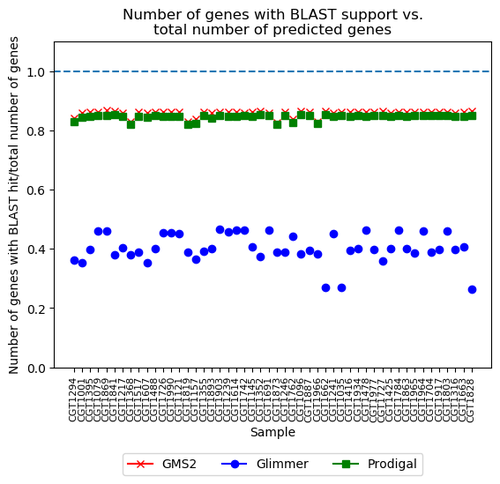
Figure 4. The ratio of each assembled genes with BLAST support from three tools.
Results: Prodigal and GMS2 perform more consistently, so the filtering does not influence the results.
- Plot bar plot of the number of predicted genes per sample
Figure 5. The number of predicted genes of each sample from GMS2, Prodigal, and Glimmer.
Results: The number of predicted genes between GMS2 and Prodigal is similar, but clearly, the Glimmer has a different number of predicted genes.
- Summary Results