Team I Genome Assembly Group
Team 1 Genome Assembly
Team members: Lawrence McKinney, Laura Mora, Jessica Mulligan, Heather Patrick, Devishi Kesar, and Cecilia (Hyeonjeong) Cheon
In-Class Presentations
File:Team 1 Genome Assembly Presentation 1.pdf
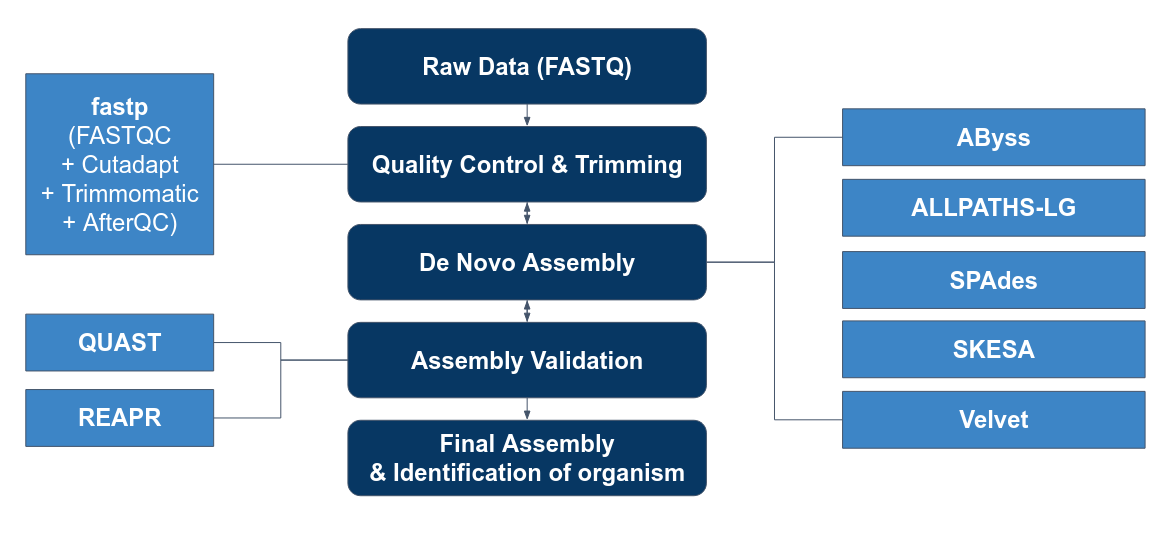
Genome Assembly Pipeline
Our Goals
1. To perform quality control on reads before and after assembling the genome.
2. To evaluate the performance of assembly tools:
* Abyss * ALLPATHS-LG * SPADES * SKESA * Velvet
3. To use the best 2 to perform de novo assembly based on the 50 isolates.
4. To send off the highest quality result to gene prediction.
References
1. Alexey Gurevich, Vladislav Saveliev, Nikolay Vyahhi, Glenn Tesler, QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies, Bioinformatics, Volume 29, Issue 8, 15 April 2013, Pages 1072–1075, https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt086
2. Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, et al. SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol. 2012;19(5):455–477. doi:10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
3. Butler, Jonathan et al. “ALLPATHS: de novo assembly of whole-genome shotgun microreads.” Genome research vol. 18,5 (2008): 810-20. doi:10.1101/gr.7337908
4. Earl, Dent et al. “Assemblathon 1: a competitive assessment of de novo short read assembly methods.” Genome research vol. 21,12 (2011): 2224-41. doi:10.1101/gr.126599.111
5. Maccallum, Iain et al. “ALLPATHS 2: small genomes assembled accurately and with high continuity from short paired reads.” Genome biology vol. 10,10 (2009): R103. doi:10.1186/gb-2009-10-10-r103
6. Miller, Jason R et al. “Assembly algorithms for next-generation sequencing data.” Genomics vol. 95,6 (2010): 315-27. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2010.03.001
7. Pritt, J., Chen, N. & Langmead, B. FORGe: prioritizing variants for graph genomes. Genome Biol 19, 220 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-018-1595-x
8. Quainoo, S., Coolen, J.P., Hijum, S.A., Huynen, M.A., Melchers, W.J., Schaik, W.V., & Wertheim, H.F. (2017). Whole-Genome Sequencing of Bacterial Pathogens: the Future of Nosocomial Outbreak Analysis. Clinical microbiology reviews, 30 4, 1015-1063 .
9. Rahman, A., Pachter, L. CGAL: computing genome assembly likelihoods. Genome Biol 14, R8 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2013-14-1-r8
10. Salzberg, Steven L et al. “GAGE: A critical evaluation of genome assemblies and assembly algorithms.” Genome research vol. 22,3 (2012): 557-67. doi:10.1101/gr.131383.111
11. Shifu Chen, Yanqing Zhou, Yaru Chen, Jia Gu; fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor, Bioinformatics, Volume 34, Issue 17, 1 September 2018, Pages i884–i890, https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560
12. Sohn, Jang-il; Nam, Jin-Wu. “The present and future of de novo whole-genome assembly”, Briefings in Bioinformatics, Vol 19.1 (2018). doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbw096
13. Souvorov A., Agarwala R., & Lipman D.J. SKESA: strategic k-mer extension for scrupulous assemblies. Genome Biology. 2018; 19(1). doi:10.1186/s13059-018-1540-z
14. Tanja Magoc, Stephan Pabinger, Stefan Canzar, Xinyue Liu, Qi Su, Daniela Puiu, Luke J. Tallon, Steven L. Salzberg, GAGE-B: an evaluation of genome assemblers for bacterial organisms, Bioinformatics, Volume 29, Issue 14, 15 July 2013, Pages 1718–1725, https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt273
15. Zerbino, D., & Birney, E. (n.d.). Velvet: de novo assembly using very short reads. Hinxton: European Bioinformatics Institute.