Team II Functional Annotation Group
Team 2: Functional Annotation
Team Members: Danielle Temples, Courtney Astore, Rhiya Sharma, Ujani Hazra, Sooyoun Oh
Introduction
What is Functional Annotation?
The practice of putting biological meaning to coding genes (genes that encode proteins) and their corresponding protein sequences. Such annotations can be derived using homology and ab initio based approaches, which will be further explained in subsequent sections.
Objective: Perform a full functional annotation on the genes and proteins determined by the Gene Prediction group that is relevant to C. jejuni
Homology Approaches
- Determine function via sequence similarity to already functionally annotated sequences
- Limited by what we already know.
Ab Initio Approaches
- Determine function via predictive model without comparing to existing sequences
- Based on laws of nature
- Difficult to verify without experiments
Data Overview
We received 50 fna and 50 faa files from the gene prediction group. The 50 fna files are multifasta files representing each genome. The 50 faa files are multifasta files representing each proteome.
Clustering
Homology Methods
Categories
Prophage:
- Play an important role in the evolution of bacterial genomes and their pathogenicity
- Can change or knock out gene functions; alter gene expression
Virulence:
- A pathogen's ability to infect or damage a host
- Ex: toxins, surface coats that inhibit phagocytosis, surface receptors that bind to host cells
Fully Automated Functional Annotation:
- Tools that annotate a spectrum of features related to the function
Antibiotic Resistance
- When bacteria develop the ability to defeat the drugs designed to kill them
- Leads to higher medical costs, prolonged hospital stays, and increased mortality
Operons:
- A functional unit of transcription and genetic regulation
- Identifying these may enhance our knowledge of gene regulation & function which is a key addition to genome annotation
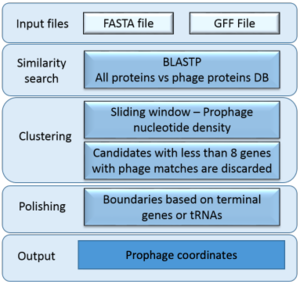
ProphET
- PROPHage Estimation Tool
- Identifies prophages in bacterial genomes with high precision and offers a fast, highly scalable alternative
- Uses three steps: similarity search, calculation of the density of prophage genes, and edge refinement
VFDB
- Virulence Factor DataBase
- Provide virulence structure features, functions, and mechanisms used to allow pathogens to conquer new niches and circumvent host defense mechanisms
- BLAST based identification of virulence genes
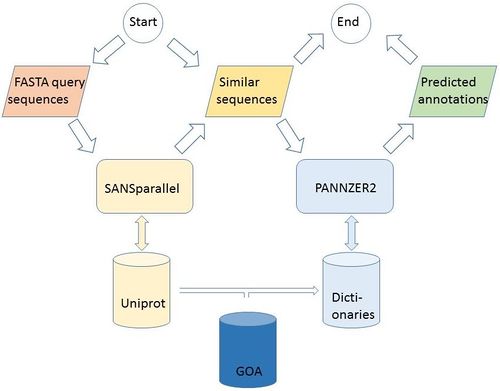
PANNZER2
- Protein ANNotation with Z-scoRE
- Provides both Gene Ontology (GO) annotations and free text description predictions
- Uses SANSparallel to perform high-performance homology searches
- Updated on a monthly schedule
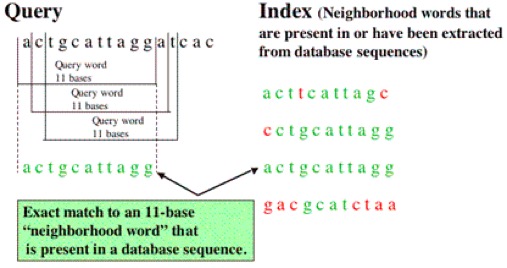
BLAST
- Basic Local Alignment Search Tool
- A database is searched for high-scoring local alignments with a query
- The annotations on the sequence that score the highest alignment are assigned to the query sequence, provided the alignment score passes a threshold
CARD
- Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database
- Provides data, models, and algorithms relating to the molecular basis of antimicrobial resistance
- Can be used for the analysis of genome sequences using the Resistance Gene Identifier