Team I Genome Assembly Group: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
=== In-Class Presentations === | === In-Class Presentations === | ||
[[File:]] | [[File: Team_1_Genome_Assembly_Presentation_1.pdf]] | ||
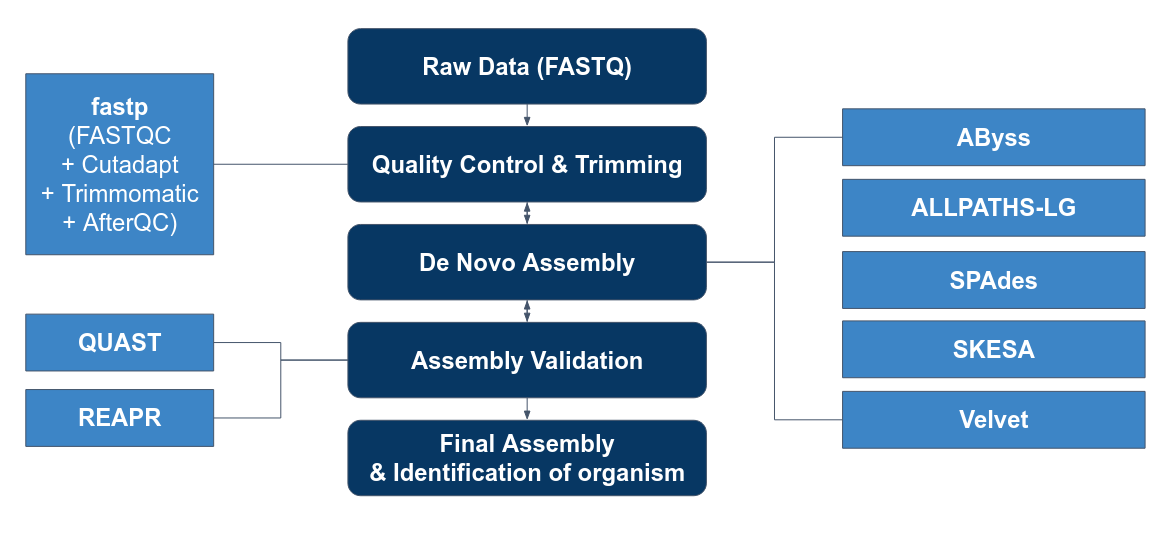
=== Genome Assembly Pipeline === | === Genome Assembly Pipeline === | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
* SKESA | * SKESA | ||
* Velvet | * Velvet | ||
3. To use the best 2 to perform de novo assembly based on the 50 isolates. | 3. To use the best 2 to perform de novo assembly based on the 50 isolates. | ||
4. To send off the highest quality result to gene prediction. | 4. To send off the highest quality result to gene prediction. | ||
=== References === | |||
Alexey Gurevich, Vladislav Saveliev, Nikolay Vyahhi, Glenn Tesler, QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies, Bioinformatics, Volume 29, Issue 8, | |||
15 April 2013, Pages 1072–1075, https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt086 | |||
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, et al. SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol. | |||
2012;19(5):455–477. doi:10.1089/cmb.2012.0021 | |||
Butler, Jonathan et al. “ALLPATHS: de novo assembly of whole-genome shotgun microreads.” Genome research vol. 18,5 (2008): 810-20. | |||
doi:10.1101/gr.7337908 | |||
Earl, Dent et al. “Assemblathon 1: a competitive assessment of de novo short read assembly methods.” Genome research vol. 21,12 (2011): 2224-41. | |||
doi:10.1101/gr.126599.111 | |||
Maccallum, Iain et al. “ALLPATHS 2: small genomes assembled accurately and with high continuity from short paired reads.” Genome biology vol. 10,10 (2009): | |||
R103. doi:10.1186/gb-2009-10-10-r103 | |||
Miller, Jason R et al. “Assembly algorithms for next-generation sequencing data.” Genomics vol. 95,6 (2010): 315-27. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2010.03.001 | |||
Pritt, J., Chen, N. & Langmead, B. FORGe: prioritizing variants for graph genomes. Genome Biol 19, 220 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-018-1595-x | |||
Quainoo, S., Coolen, J.P., Hijum, S.A., Huynen, M.A., Melchers, W.J., Schaik, W.V., & Wertheim, H.F. (2017). Whole-Genome Sequencing of Bacterial Pathogens: | |||
the Future of Nosocomial Outbreak Analysis. Clinical microbiology reviews, 30 4, 1015-1063 . | |||
Rahman, A., Pachter, L. CGAL: computing genome assembly likelihoods. Genome Biol 14, R8 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2013-14-1-r8 | |||
Salzberg, Steven L et al. “GAGE: A critical evaluation of genome assemblies and assembly algorithms.” Genome research vol. 22,3 (2012): 557-67. | |||
doi:10.1101/gr.131383.111 | |||
Shifu Chen, Yanqing Zhou, Yaru Chen, Jia Gu; fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor, Bioinformatics, Volume 34, Issue 17, 1 September 2018, Pages | |||
i884–i890, https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560 | |||
Sohn, Jang-il; Nam, Jin-Wu. “The present and future of de novo whole-genome assembly”, Briefings in Bioinformatics, Vol 19.1 (2018). | |||
doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbw096 | |||
Souvorov A., Agarwala R., & Lipman D.J. SKESA: strategic k-mer extension for scrupulous assemblies. Genome Biology. 2018; 19(1). | |||
doi:10.1186/s13059-018-1540-z | |||
Tanja Magoc, Stephan Pabinger, Stefan Canzar, Xinyue Liu, Qi Su, Daniela Puiu, Luke J. Tallon, Steven L. Salzberg, GAGE-B: an evaluation of genome assemblers | |||
for bacterial organisms, Bioinformatics, Volume 29, Issue 14, 15 July 2013, Pages 1718–1725, https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt273 | |||
Zerbino, D., & Birney, E. (n.d.). Velvet: de novo assembly using very short reads. Hinxton: European Bioinformatics Institute. | |||
Revision as of 17:52, 29 January 2020
Team 1 Genome Assembly
In-Class Presentations
File:Team 1 Genome Assembly Presentation 1.pdf
Genome Assembly Pipeline
Our Goals
1. To perform quality control on reads before and after assembling the genome. 2. To evaluate the performance of assembly tools:
* Abyss * ALLPATHS-LG * SPADES * SKESA * Velvet
3. To use the best 2 to perform de novo assembly based on the 50 isolates.
4. To send off the highest quality result to gene prediction.
References
Alexey Gurevich, Vladislav Saveliev, Nikolay Vyahhi, Glenn Tesler, QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies, Bioinformatics, Volume 29, Issue 8, 15 April 2013, Pages 1072–1075, https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt086 Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, et al. SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol. 2012;19(5):455–477. doi:10.1089/cmb.2012.0021 Butler, Jonathan et al. “ALLPATHS: de novo assembly of whole-genome shotgun microreads.” Genome research vol. 18,5 (2008): 810-20. doi:10.1101/gr.7337908 Earl, Dent et al. “Assemblathon 1: a competitive assessment of de novo short read assembly methods.” Genome research vol. 21,12 (2011): 2224-41. doi:10.1101/gr.126599.111 Maccallum, Iain et al. “ALLPATHS 2: small genomes assembled accurately and with high continuity from short paired reads.” Genome biology vol. 10,10 (2009): R103. doi:10.1186/gb-2009-10-10-r103 Miller, Jason R et al. “Assembly algorithms for next-generation sequencing data.” Genomics vol. 95,6 (2010): 315-27. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2010.03.001 Pritt, J., Chen, N. & Langmead, B. FORGe: prioritizing variants for graph genomes. Genome Biol 19, 220 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-018-1595-x Quainoo, S., Coolen, J.P., Hijum, S.A., Huynen, M.A., Melchers, W.J., Schaik, W.V., & Wertheim, H.F. (2017). Whole-Genome Sequencing of Bacterial Pathogens: the Future of Nosocomial Outbreak Analysis. Clinical microbiology reviews, 30 4, 1015-1063 . Rahman, A., Pachter, L. CGAL: computing genome assembly likelihoods. Genome Biol 14, R8 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2013-14-1-r8 Salzberg, Steven L et al. “GAGE: A critical evaluation of genome assemblies and assembly algorithms.” Genome research vol. 22,3 (2012): 557-67. doi:10.1101/gr.131383.111 Shifu Chen, Yanqing Zhou, Yaru Chen, Jia Gu; fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor, Bioinformatics, Volume 34, Issue 17, 1 September 2018, Pages i884–i890, https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560 Sohn, Jang-il; Nam, Jin-Wu. “The present and future of de novo whole-genome assembly”, Briefings in Bioinformatics, Vol 19.1 (2018). doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbw096 Souvorov A., Agarwala R., & Lipman D.J. SKESA: strategic k-mer extension for scrupulous assemblies. Genome Biology. 2018; 19(1). doi:10.1186/s13059-018-1540-z Tanja Magoc, Stephan Pabinger, Stefan Canzar, Xinyue Liu, Qi Su, Daniela Puiu, Luke J. Tallon, Steven L. Salzberg, GAGE-B: an evaluation of genome assemblers for bacterial organisms, Bioinformatics, Volume 29, Issue 14, 15 July 2013, Pages 1718–1725, https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt273 Zerbino, D., & Birney, E. (n.d.). Velvet: de novo assembly using very short reads. Hinxton: European Bioinformatics Institute.