Team I Functional Annotation Group: Difference between revisions
| Line 214: | Line 214: | ||
[27] Buchfink, B., Xie, C., & Huson, D. H. (2015). Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nature methods, 12(1), 59. | [27] Buchfink, B., Xie, C., & Huson, D. H. (2015). Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nature methods, 12(1), 59. | ||
[28] Pearson W. R. (2013). An introduction to sequence similarity ("homology") searching. Current protocols in bioinformatics, Chapter 3, Unit3.1. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471250953.bi0301s42 | |||
Revision as of 21:01, 29 March 2020
Team 1 Functional Annotation
Team members: Maria Ahmad, Shuheng Gan, Manasa Vegesna, Hyeonjeong Cheon, and Kenji Gerhardt
Introduction
Background
Functional annotation is the process of associating predicted genes with their functional role in a cell. This includes the type of gene (translated/untranslated), their location within the cell, and their chemical and biological roles. These can be derived both by comparison to similar, already annotated genes with known (or anticipated) functions, or through ab initio annotation that relies on existing models, but which does not rely on databases of other annotated genes.
Objective
Our goal in this step is to functionally annotate the genes supplied to us by the gene prediction group.
Data
The genomes supplied to us were identified during assembly as E. coli. E. coli is the most highly studied microorganism: at present, NCBI contains 1072 complete E. coli genomes in its genome database, along with thousands of additional chromosomes, contigs, and scaffolds. This depth of study extends to its genes, where multiple pathogenic strains are identified and characterized well.
Pipeline
Pipeline image will be inserted
Clustering
Protein clustering is the task of reducing a large number of sequences down to a smaller set of cluster representatives. A cluster representative is a single sequence whose functional characteristics are similar/the same as the other sequences contained within the cluster. The point of clustering is to produce a set of fewer, and thereby computationally easier/quicker to annotate, representative sequences whose subsequent annotation can then be applied to the other members of the cluster they represent.
In order to cluster sequences, the tool we selected for our final pipeline (USearch) sets a boundary based on percent identity between sequences in a dataset. This boundary at which sequences are clustered is the minimum threshold of difference between the two sequences for them to be included in the same cluster; sequences more dissimilar than the boundary will either be clustered with a different sequence, or will become their own cluster if they fail to cluster with any other sequences. As a result, the ideal boundary is one which captures sequences sharing function within single clusters, and does not cluster sequences with different functions in the same cluster.
In practice, such an ideal boundary will always be beset with problems: very similar sequences may have different functions, very disparate sequences may share function, and the necessary similarity to share function between proteins will vary by protein. Further, due to the degeneracy of the translation between nucleotides and amino acids, sequences which are similar at the protein level may be highly divergent at the nucleotide level, excluding the untranslated untranslated proteins. As a result, performance will be imperfect, and a decision between accuracy of clustering results and efficacy of clustering has to be made.
For the purposes of our work, we decided to cluster amino acids rather than nucleotide sequences for the majority of our tasks. Protein function is ultimately dictated by amino acid sequence, at least insofar as the data that annotation tools receive from a user. Although most tools are designed to work both with nucleotide sequences and amino acid sequences, clustering nucleotide sequences with the aim of clustering protein function is a largely misguided effort.
NCBI guidelines [28] indicate that protein functional similarity is very likely at 40% amino acid identity. However, since our task is performed in the context of 50 samples of the same species, we decided upon a much more conservative 70% amino acid identity boundary to cluster our sequences. This produces more clusters than is likely necessary, but is less likely to cluster proteins with disparate functions than a more lenient standard.
USearch
The tool our pipeline uses is called USearch. Among other functions, USearch performs sequence clustering using a greedy agglomerative algorithm, meaning it creates clusters and assigns cluster identity in the order of input sequences.
While it is possible that this order-dependent behavior may result in a sequence being assigned to a cluster that it does not ideally join, the conservative cutoff for sequence similarity that we selected makes it unlikely that this will affect function. More probably, a sequence will be assigned to one of a few similar clusters which properly should be joined, as the multiple clusters share the same function.
The result of USearch is pair of files: one tab-separated file listing the cluster representative, the sequences belonging to that representative and their identity to the representative, and a second listing just the representative sequences in FASTA format, which is friendly to annotation tools.
Methods
Ab-initio Approach
Ab-Initio Tools predict and annotate different regions of the prokaryotic genome using 1) sequence composition, 2) likelihoods within the gene models, 3) gene content, and 4) ignal Detection. Ab-Initio Approach can be used for finding new genes, and no external data or evidence is needed for the prediction. However, it is limited by the presence of False Positives in the predicted data as well as over-prediction of small genes.
PSORTb
remove if not needed
SignalP
remove if not needed
LipoP
remove if not needed
TatP
remove if not needed
TMHMM
remove if not needed
Phobius
remove if not needed
CRISPRCasFinder
remove if not needed
PILER-CR
remove if not needed
CRT
remove if not needed
Homology-based Tools
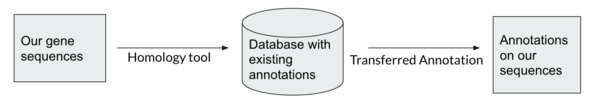
Homology between genes means they share ancestry. Homologous genes that have recently diverged usually share function. We are looking to transfer annotation on known genes to our predicted genes by finding homology genes. Gene databases are collections of annotated genes. When we search a gene against a database, the search is looking for homology between our gene sequences and those in the database to determine what our genes’ function will be.
Homology-based tools are more accurate and reliable than Ab-initio tools, and can be targeted for specific purposes, e.g. antibiotic resistance genes. However, homology tools are dependent on existing annotations and on what databases are being searched.
Prokka
- Prokka is a command line software tool for the rapid annotation of prokaryotic genomes in about 10 min on a desktop computer.
- Features include coding sequences (Prodigal), rRNA (RNAmmer), tRNA (Aragorn), signal peptides (SignalP), and non-coding RNA (Infernal) and including these options are flexible.
- The typical input file is FASTA format and output contains 12 output files: .err, .fsa, .sqn, .val, .faa, .gbf, .tbl, .ffn, .gff, .tsv, .fna, .log, .txt
Command:
prokka <input_file> --outdir <output directory> --prefix <file prefixes> --kingdom Bacteria --locustag --norrna --notrna
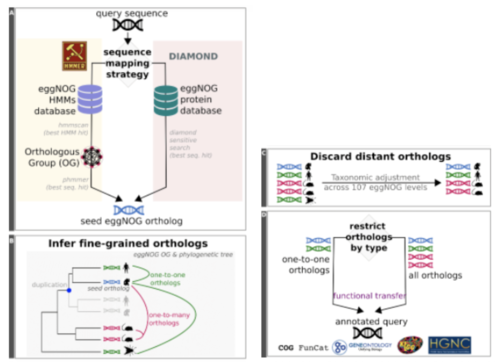
EggNOG-mapper
- Performes fast functional annotation of genes and proteins
- Uses precomputed orthologous groups and phylogenies from the eggNOG database which consists of Orthologous Groups( OGs) of proteins at taxonomic levels.
- Has a mode recommended for large datasets called DIAMOND. Diamond mode searches for the best seed ortholog located in the eggNOG protein database, and is faster than the other mode HMM. The HMM mode is comprised of a collection of precompiled hidden Markov models.
To download bacteria databases:
python2.7 download_eggnog_data.py bact
Command:
python emapper.py -i <input_file> --output <output_file> -m diamond -d bact -o <output directory>
InterProScan
- InterProScan is function annotation tool that scans sequences against InterPro protein signature databases. It classifies proteins into families and predict domains and important sites.
- Signatures are predictive models constructed from multiple sequence alignments that can be used to classify proteins. Using protein signatures is often a more sensitive way of identifying protein function than pairwise sequence similarity searches, such as BLAST.
- InterPro combines four types of protein signatures (patterns, profiles, fingerprints and HMMs) from multiple databases.
Download (https://github.com/ebi-pf-team/interproscan/wiki/HowToDownload)
# download interproscan and most database wget ftp://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/software/unix/iprscan/5/5.42-78.0/interproscan-5.42-78.0-64-bit.tar.gz wget ftp://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/software/unix/iprscan/5/5.42-78.0/interproscan-5.42-78.0-64-bit.tar.gz.md5 md5sum -c interproscan-5.42-78.0-64-bit.tar.gz.md5 # download Panther cd [InterProScan5 home]/data/ wget ftp://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/software/unix/iprscan/5/data/panther-data-14.1.tar.gz wget ftp://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/software/unix/iprscan/5/data/panther-data-14.1.tar.gz.md5 md5sum -c panther-data-14.1.tar.gz.md5
Requirement (https://github.com/ebi-pf-team/interproscan/wiki/InstallationRequirements)
- - Perl 5.22
- - Python 3
- - Java 11
Command
interproscan.sh -i <input_file_name> -dp -d <output_directory> -appl <databases_you_choose> -f <output_format> -t <sequence_type>
- parameters:
- -d: optional, default current directory [./]
- -appl: optional, default all 14 databases [CDD-3.17,Coils-2.2.1,Gene3D-4.2.0,Hamap-2020_01,MobiDBLite-2.0,PANTHER-14.1,Pfam-32.0,PIRSF-3.02,
- PRINTS-42.0,ProSitePatterns-2019_11,ProSiteProfiles-2019_11,SFLD-4,SMART-7.1,SUPERFAMILY-1.75,TIGRFAM-15.0]
- -f: optional, default [gff3, tsv, and xml for protein | gff3 and xml for nucleotide]
- -t: optional, n/p, default protein [p]
- runtime of default setting: ~12h
DeepARG
DeepARG is a deep learning tool that annotate antibiotic resistance genes in metagenomes. It is composed of two models for two types of input: DeepARG-SS for short sequence reads from Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) technologies such as Ilummina and DeepARG-LS for long gene-like sequences from assembled samples.
Download
git clone https://bitbucket.org/gusphdproj/deeparg-ss
Requirement
- - Python 2.7
Command
python ./deepARG.py --align --genes --type prot --input <gene-like_sequences_fasta_file> --out <output_file_name>
- output:
- - output_file_name.align.daa, DIAMOND alignment archive
- - output_file_name.align.daa.tsv, tabular format. Default: qseqid sseqid pident length mismatch gapopen qstart qend sstart send evalue bitscore
- - output_file_name.mapping.ARG, contains the sequences with a probability >= --prob (0.8 default)
- - output_file_name.mapping.potential.ARG, contains the sequences with a probability < --prob (0.8 default)
Results
Reference
[1] Joshi, T., & Xu, D. (2007). Quantitative assessment of relationship between sequence similarity and function similarity. BMC genomics, 8(1), 222.
[2] Zou, Q., Lin, G., Jiang, X., Liu, X., & Zeng, X. (2020). Sequence clustering in bioinformatics: an empirical study. Briefings in bioinformatics, 21(1), 1-10.
[3] Nielsen, H., Tsirigos, K. D., Brunak, S., & von Heijne, G. (2019). A brief history of protein sorting prediction. The protein journal, 38(3), 200-216.
[4] Viklund, H., & Elofsson, A. (2004). Best α‐helical transmembrane protein topology predictions are achieved using hidden Markov models and evolutionary information. Protein Science, 13(7), 1908-1917.
[5] Romine, M. F. (2011). Genome-wide protein localization prediction strategies for gram negative bacteria. BMC genomics, 12(S1), S1.
[6] Yu, N. Y., Wagner, J. R., Laird, M. R., Melli, G., Rey, S., Lo, R., ... & Brinkman, F. S. (2010). PSORTb 3.0: improved protein subcellular localization prediction with refined localization subcategories and predictive capabilities for all prokaryotes. Bioinformatics, 26(13), 1608-1615.
[7] Armenteros, J. J. A., Tsirigos, K. D., Sønderby, C. K., Petersen, T. N., Winther, O., Brunak, S., ... & Nielsen, H. (2019). SignalP 5.0 improves signal peptide predictions using deep neural networks. Nature biotechnology, 37(4), 420-423.
[8] Juncker, A. S., Willenbrock, H., Von Heijne, G., Brunak, S., Nielsen, H., & Krogh, A. (2003). Prediction of lipoprotein signal peptides in Gram‐negative bacteria. Protein Science, 12(8), 1652-1662.
[9] Bendtsen, J. D., Nielsen, H., Widdick, D., Palmer, T., & Brunak, S. (2005). Prediction of twin-arginine signal peptides. BMC bioinformatics, 6(1), 167.
[10] Käll, L., Krogh, A., & Sonnhammer, E. L. (2004). A combined transmembrane topology and signal peptide prediction method. Journal of molecular biology, 338(5), 1027-1036.
[11] Krogh, A., Larsson, B., Von Heijne, G., & Sonnhammer, E. L. (2001). Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. Journal of molecular biology, 305(3), 567-580.
[12] Couvin, D., Bernheim, A., Toffano-Nioche, C., Touchon, M., Michalik, J., Néron, B., ... & Pourcel, C. (2018). CRISPRCasFinder, an update of CRISRFinder, includes a portable version, enhanced performance and integrates search for Cas proteins. Nucleic acids research, 46(W1), W246-W251.
[13] Mao, F., Dam, P., Chou, J., Olman, V., & Xu, Y. (2009). DOOR: a database for prokaryotic operons. Nucleic acids research, 37(Database issue), D459–D463. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn757
[14] Chen, L., Yang, J., Yu, J., Yao, Z., Sun, L., Shen, Y., & Jin, Q. (2005). VFDB: a reference database for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic acids research, 33(Database issue), D325–D328. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki008
[15] eggNOG 4.5: a hierarchical orthology framework with improved functional annotations for eukaryotic, prokaryotic and viral sequences. Jaime Huerta-Cepas, Damian Szklarczyk, Kristoffer Forslund, Helen Cook, Davide Heller, Mathias C. Walter, Thomas Rattei, Daniel R. Mende, Shinichi Sunagawa, Michael Kuhn, Lars Juhl Jensen, Christian von Mering, and Peer Bork.Nucl. Acids Res. (04 January 2016) 44 (D1): D286-D293. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1248
[16] McArthur et al. 2013. The Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 57, 3348-57.
[17] Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jan;37(Database issue):D443-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn656. Epub 2008 Oct 2.
[18] Arndt, D., Grant, J., Marcu, A., Sajed, T., Pon, A., Liang, Y., Wishart, D.S. (2016) PHASTER: a better, faster version of the PHAST phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res., 2016 May 3.
[19] Arango-Argoty, G., Garner, E., Pruden, A. et al. DeepARG: a deep learning approach for predicting antibiotic resistance genes from metagenomic data. Microbiome 6, 23 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-018-0401-z
[20] Ashburner et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet. May 2000;25(1):25-9.
[21] Prediction of lipoprotein signal peptides in Gram-negative bacteria.A. S. Juncker, H. Willenbrock, G. von Heijne, H. Nielsen, S. Brunak and A. Krogh.Protein Sci. 12(8):1652-62, 2003
[22] Huerta-Cepas, J., Forslund, K., Coelho, L. P., Szklarczyk, D., Jensen, L. J., Von Mering, C., & Bork, P. (2017). Fast genome-wide functional annotation through orthology assignment by eggNOG-mapper. Molecular biology and evolution, 34(8), 2115-2122.
[23] Seemann, T. (2014). Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics, 30(14), 2068-2069.
[24] Arango-Argoty, G., Garner, E., Pruden, A., Heath, L. S., Vikesland, P., & Zhang, L. (2018). DeepARG: a deep learning approach for predicting antibiotic resistance genes from metagenomic data. Microbiome, 6(1), 1-15.
[25] Finn, R. D., Attwood, T. K., Babbitt, P. C., Bateman, A., Bork, P., Bridge, A. J., ... & Gough, J. (2017). InterPro in 2017—beyond protein family and domain annotations. Nucleic acids research, 45(D1), D190-D199.
[26] Camacho, C., Coulouris, G., Avagyan, V., Ma, N., Papadopoulos, J., Bealer, K., & Madden, T. L. (2009). BLAST+
[27] Buchfink, B., Xie, C., & Huson, D. H. (2015). Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nature methods, 12(1), 59.
[28] Pearson W. R. (2013). An introduction to sequence similarity ("homology") searching. Current protocols in bioinformatics, Chapter 3, Unit3.1. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471250953.bi0301s42